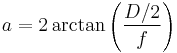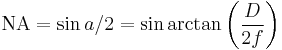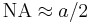Angular aperture
The angular aperture of a lens is the apparent angle of the lens aperture as seen from the focal point:
where
 is the focal length
is the focal length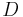 is the diameter of the aperture.
is the diameter of the aperture.
Relation to numerical aperture
In a medium with an index of refraction close to 1, such as air, the angular aperture is approximately equal to twice the numerical aperture of the lens.[1]
Formally, the numerical aperture in air is:
In the paraxial approximation, with a small aperture, 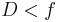 :
:
References
- ^ Albert Abraham Michelson (1995). Studies in Optics. Courier Dover. pp. 32. ISBN 0486687007. http://books.google.com/books?id=m2tUZ4_8WGMC&pg=PA32&dq=%22Angular+aperture%22&ie=ISO-8859-1&output=html.